HAVEN Research Group
Research Projects’ Sponsors






Current Focus of Research (Ongoing)
[Research Project 3]
Evolutionary Large Language Models for Hardware Security
This research explores the transformative role of Large Language Models (LLMs) in enhancing hardware security throughout the design lifecycle. By leveraging prompt engineering and fine-tuning, LLMs can improve hardware reliability, automate functional and security verification, and detect vulnerabilities early in the design phase—mitigating costly post-fabrication risks. Additionally, this work investigates LLM-driven automation in the IC supply chain, from secure RTL design to synthesis and physical design flows, ensuring robust protection against emerging threats while maintaining system confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad).

Selected Publications:
[Research Project 2]
Advancing System Security Solutions for Heterogeneous Integration
As Moore’s Law slows and Dennard scaling faces challenges, the semiconductor industry is shifting towards advanced packaging and heterogeneous integration (HI) as the next technological frontier. This research investigates the Security of Heterogeneous Integration (SHI) by extending proven security solutions from 2D SoCs to HI-based System-in-Package (SiP) architectures. We explore trust validation and attack mitigation strategies across the SiP supply chain, addressing emerging security concerns such as fault injection, secure activation and locking, and rule-based security verification. Our work aligns with the NIST MAPT Roadmap and SRC’s Decadal Plan, contributing to the development of end-to-end secure heterogeneous integration for the future of microelectronics.

Selected Publications:
[Research Project 1]
IC/IP Protection: Advanced Logic Locking and Secure Activation
With the increasing complexity and globalization of the IC supply chain, design teams must collaborate with multiple third parties, often in untrusted environments. This exposes hardware security threats such as IP piracy and IC overproduction. Logic locking is a promising countermeasure that enables designers to safeguard designs throughout the supply chain while allowing post-manufacturing activation. This research focuses on: (1) developing robust locking mechanisms, (2) ensuring secure activation without secret leakage, (3) enhancing resilience against evolving attack models, and (4) adapting logic locking for emerging technologies and new fabrication environments. Additionally, we assess the EDA compatibility and commercialization potential of advanced locking solutions, ensuring practical deployment in modern semiconductor workflows.
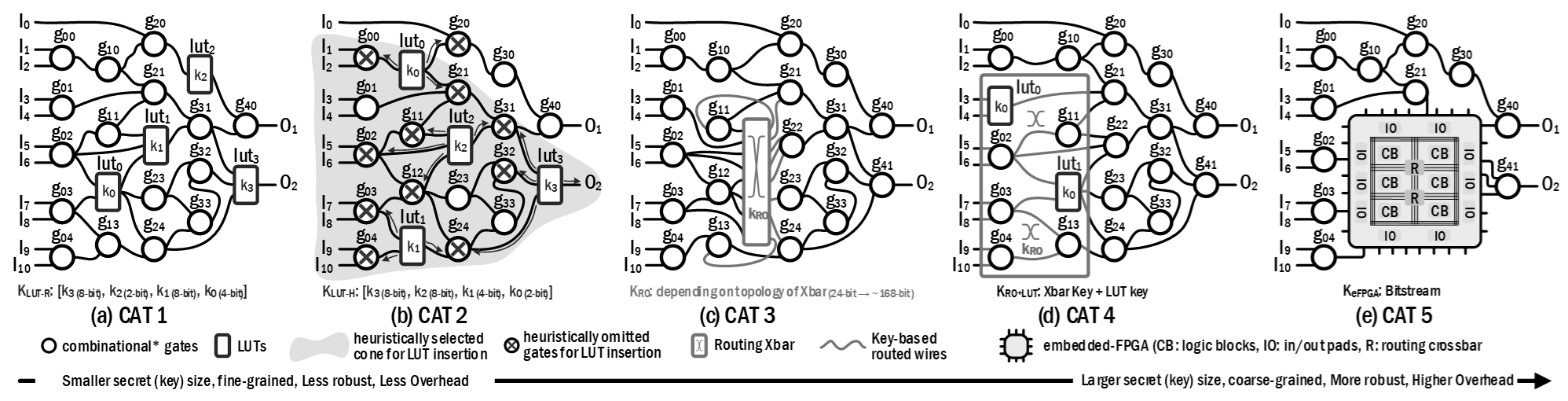
Selected Publications:
Previous/Other Focus of Research (Previous)
[Research Project 4]
Security by Construction: Early Stage Security-aware IC Design and Implementation
The shift towards high-level synthesis (HLS) for SoC design enables faster development, reduced verification efforts, and lower costs. However, security concerns such as information leakage and side-channel vulnerabilities can be inadvertently introduced during the HLS translation process. This research establishes early-stage security-aware design methodologies, integrating secure design rule checking at the high-level description (C/C++). By leveraging techniques such as information flow tracking, path decoupling, and security-aware resource utilization, we aim to embed security constraints early in the IC design lifecycle—ensuring robustness against emerging threats before RTL and gate-level synthesis.

Selected Publications:
[Research Project 3]
Forward Trust in IC Supply Chain: Enabling Secure Authentication and Provisioning
This research establishes forward trust by integrating secure authentication and provisioning throughout the IC lifecycle. We focus on: (1) Secure Design for Testability, safeguarding scan chains during testing, (2) Forward Implication, ensuring security at every stage of the supply chain, (3) Secure Communication via Primitives, implementing authenticated encryption for remote activation in 3D designs and IoT applications, and (4) Uniqueness for Activation, creating tamper-resistant activation mechanisms against hammering attacks. By fortifying each step of the IC supply chain, this work builds a comprehensive security framework, mitigating threats from reverse engineering to probing, and ensuring trust in next-generation semiconductor technologies.
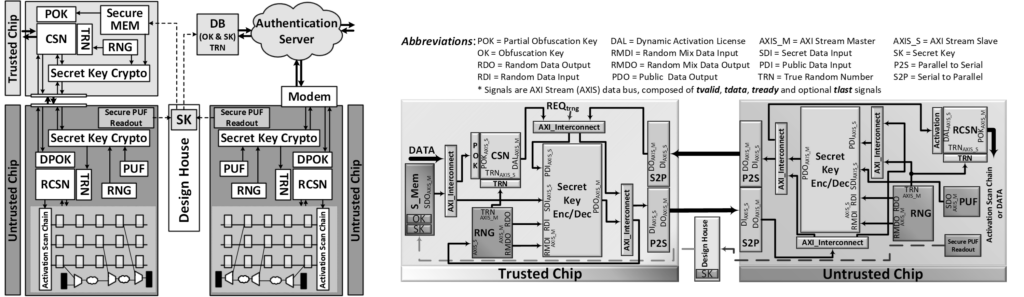
Selected Publications:
[Research Project 2]
Towards Low Power Interconnection Architectures: Network-on-Chip Optimization
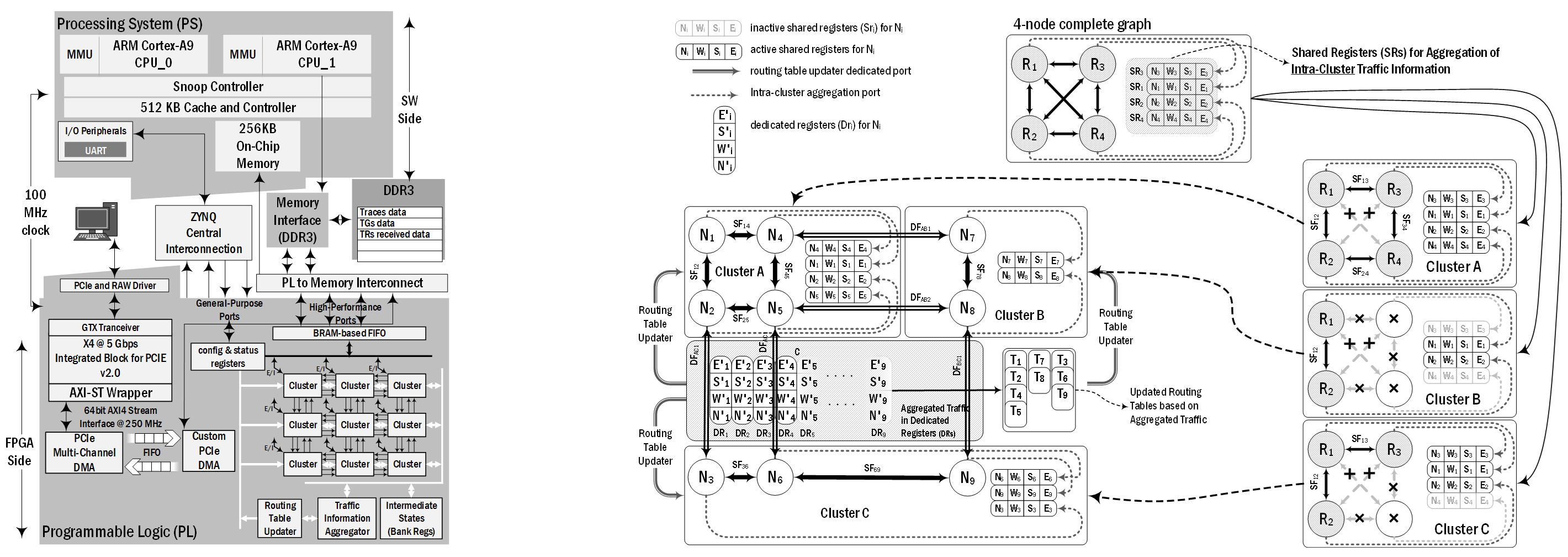
As Network-on-Chip (NoC) architectures become the backbone of modern multi-core and many-core processors, optimizing their power efficiency is crucial for sustainable high-performance computing. This research focuses on minimizing static power consumption by addressing inefficiencies in NoC router micro-architectures. By leveraging power-gating techniques, we develop deterministic routing algorithms that strategically reduce packet encounters with power-gated routers, maximizing router idleness and energy savings. Additionally, we optimize routing tables to establish dedicated communication paths, ensuring efficient router utilization. These advancements significantly lower leakage power, reduce latency, and improve overall energy efficiency, making NoC architectures more scalable, cost-effective, and practical for next-generation computing systems.

[Research Project 1]
FPGA-based Computer Architecture (Interconnection) Acceleration Solutions
FPGA-based acceleration is revolutionizing computer architecture, offering high-performance solutions for algorithm acceleration, AI/ML processing, cryptography, and networking. This research focuses on FPGA-based NoC simulation and emulation, addressing the critical need for cycle-accurate, high-performance, and flexible NoC evaluation tools. By leveraging FPGA reconfigurability, we optimize NoC emulation by offloading non-computation-intensive components (e.g., Traffic Generators and Receptors) to software for greater programmability, while retaining computation-heavy processes on FPGA for accelerated execution. This approach enhances emulation performance, improves NoC design optimization, and advances application-specific architectures, contributing to the next generation of high-performance computing and multiprocessor system-on-chip (MPSoC) technologies.